成果展示
主窗口如下:
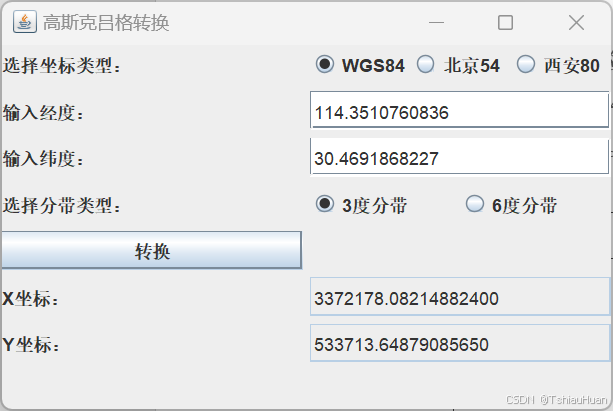
验证结果如下(以WGS84坐标纬度为30.4691868227°,经度为114.3510760836°,选择3度分带为例):
详细过程待补充
代码如下:
gs.java:
//类的定义及成员变量
public class gs {
private double PI=3.1415926;
private double a, b, e1, e2, A1, B1, C1, D1, E1, F1, G1;//用于存储椭球的参数和中间计算值
// 构造函数初始化椭球参数
public gs(double a1, double b1) {
this.a = a1;
this.b = b1;
this.e1 = Math.sqrt((a1 * a1 - b1 * b1) / (a1 * a1));//计算椭球的第一偏心率
this.e2 = Math.sqrt((a1 * a1 - b1 * b1) / (b1 * b1));//计算椭球的第二偏心率
//计算各参数 A1, B1, C1, D1, E1, F1, G1
this.A1 = 1.0 +3.0/4.0*Math.pow(e1,2)+45.0/64.0*Math.pow(e1,4)+175.0/256.0*Math.pow(e1,6)+
11025.0/16384.0*Math.pow(e1,8)+43659.0/65536.0*Math.pow(e1,10)+693693.0/1048576.0*Math.pow(e1,12);
this.B1 = 3.0/8.0*Math.pow(e1,2)+15.0/32.0*Math.pow(e1,4)+525.0/1024.0*Math.pow(e1,6)+2205.0/4096.0*Math.pow(e1,8)
+72765.0/131072.0*Math.pow(e1,10)+297297.0/524288.0*Math.pow(e1,12);
this.C1 = 15.0/256.0*Math.pow(e1,4)+105.0/1024.0*Math.pow(e1,6)+2205.0/16384.0*Math.pow(e1,8)
+10396.0/65536.0*Math.pow(e1,10)+1486485.0/8388608.0*Math.pow(e1,12);
this.D1 = 35.0/3072.0*Math.pow(e1,6)+105.0/4096.0*Math.pow(e1,8)+10395.0/262144.0*Math.pow(e1,10)
+55055.0/1048576.0*Math.pow(e1,12);
this.E1 = 315.0/131072.0*Math.pow(e1,8)+3465.0/524288.0*Math.pow(e1,10)+99099.0/8388608.0*Math.pow(e1,12);
this.F1 = 693.0/1310720.0*Math.pow(e1,10)+9909.0/5242880.0*Math.pow(e1,12);
this.G1 = 1001.0/8388608.0*Math.pow(e1,12);
}
// 计算卯酉圈曲率半径,输入参数 B 是纬度(以弧度为单位)
private double CalculateN(double B) {
return a/Math.sqrt(1.0 - e1 * e1 * Math.sin(B) * Math.sin(B));
}
// 计算中央子午线弧长,输入参数 B 是纬度(以弧度为单位)
private double CalculateX(double B) {
return a*(1.0-e1*e1)*(A1*B-B1*Math.sin(2*B)+C1*Math.sin(4*B)-D1*Math.sin(6*B)+E1*Math.sin(8*B)-
F1*Math.sin(10*B)+G1*Math.sin(12*B));
}
// 3度分带转换x值求解
public double gsklv3gtransformX(double Lon, double Lat) {
double L0 = 3.0 * (Math.floor((Lon-1.5) / 3.0) + 1.0); //3度分带中央经线
double l = (Lon - L0) * PI / 180.0; //当地经度减去中央子午线经度 (转换为弧度)
double B = Lat * PI / 180.0; //纬度(转换为弧度)
double N = CalculateN(B); //计算曲率半径
double X = CalculateX(B); //计算弧长
double t = Math.tan(B);
double η2 = this.e2 * this.e2 * Math.cos(B) * Math.cos(B);
return X +N*t*Math.cos(B)*Math.cos(B)*l*l*(0.5+(1.0/24.0)*(5.0-t*t+9.0*η2+4.0*Math.pow(η2,2))*
Math.pow(l*Math.cos(B),2)+1.0/720.0*(61.0-58.0*t*t+Math.pow(t,4))*Math.pow(l*Math.cos(B),4));
}
// 3度分带转换y值求解
public double gsklv3gtransformY(double Lon, double Lat) {
double L0 = 3.0 *( Math.floor((Lon-1.5) / 3.0) + 1.0); //3度分带中央经线
double l = (Lon - L0) * PI / 180.0; //当地经度减去中央子午线经度 (转换为弧度)
double B = Lat * PI / 180.0; //纬度(转换为弧度)
double N = CalculateN(B); //计算曲率半径
double t = Math.tan(B);
double η2 = this.e2 * this.e2 * Math.cos(B) * Math.cos(B);
return 500000.0 + N * Math.cos(B)*l*(1.0+(1.0/6.0)*(1.0-t*t+η2)*Math.cos(B)*Math.cos(B)*l*l+(1.0/120.0)*
(5.0-18.0*(t*t)+Math.pow(t,4)+14.0*(η2)-58.0*(t*t*η2))*Math.pow(Math.cos(B),4)*Math.pow(l,4));
}
// 6度分带转换x值求解
public double gsklv6gtransformX(double Lon, double Lat) {
double L0 = 6.0 * (Math.floor(Lon / 6.0) + 1.0)-3.0; //6度分带中央经线
double l = (Lon - L0) * PI / 180.0; //当地经度减去中央子午线经度 (转换为弧度)
double B = Lat * PI / 180.0; //纬度(转换为弧度)
double N = CalculateN(B); //计算曲率半径
double X = CalculateX(B); //计算弧长
double t = Math.tan(B);
double η2 = this.e2*this.e2 * Math.cos(B) * Math.cos(B);
return X + N*t*Math.cos(B)*Math.cos(B)*l*l*(0.5+(1.0/24.0)*(5.0-t*t+9.0*η2+4.0*Math.pow(η2,2))*
Math.pow(l*Math.cos(B),2)+1.0/720.0*(61.0-58.0*t*t+Math.pow(t,4))*Math.pow(l*Math.cos(B),4));
}
// 6度分带转换y值求解
public double gsklv6gtransformY(double Lon, double Lat) {
double L0 = 6.0 * (Math.floor(Lon / 6.0) + 1.0)-3.0; //6度分带中央经线
double l = (Lon - L0) * PI / 180.0; //当地经度减去中央子午线经度 (转换为弧度)
double B = Lat * PI / 180.0; //纬度(转换为弧度)
double N = CalculateN(B); //计算曲率半径
double η2 = this.e2* this.e2 * Math.cos(B) * Math.cos(B);
double t = Math.tan(B);
return 500000.0 + N * Math.cos(B)*l*(1.0+(1.0/6.0)*(1.0-t*t+η2)*Math.cos(B)*Math.cos(B)*l*l+(1.0/120.0)*
(5.0-18.0*(t*t)+Math.pow(t,4)+14.0*(η2)-58.0*(t*t*η2))*Math.pow(Math.cos(B),4)*Math.pow(l,4));
}
}gsklMain.java:
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class gsklMain {
public static void main(String args[]) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("高斯克吕格转换");
frame.setLocation(600,300); //设置窗口在屏幕上的位置
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); //设置窗口的默认关闭操作,当用户点击关闭按钮时,程序将退出
frame.getContentPane().add(new gsklWindow()); //获取窗口的内容面板,并添加一个 gsklWindow 实例
frame.pack(); //调整窗口大小,以适应其内容的大小和布局
frame.setVisible(true); //设置窗口为可见
}
}gsklWindow.java:
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class gsklWindow extends JPanel {
//声明一组私有成员变量,用于创建不同的图形组件,如单选按钮、文本字段和按钮
private JRadioButton radioWGS84, radioBeijing54, radioXian80;
private JTextField textLon, textLat, textX, textY;
private JButton buttonTransform;
private JRadioButton radio3Degree, radio6Degree;
public gsklWindow() { //构造函数
setLayout(new GridLayout(8, 2, 5, 5)); //设置面板的布局为 8 行 2 列的网格布局,每个单元格之间有 5 像素的间距
//创建三个单选按钮,用于选择坐标类型
radioWGS84 = new JRadioButton("WGS84");
radioBeijing54 = new JRadioButton("北京54");
radioXian80 = new JRadioButton("西安80");
//创建一个按钮组 bgCoordinate,并将这三个单选按钮添加到按钮组中,以确保只能选择其中一个
ButtonGroup bgCoordinate = new ButtonGroup();
bgCoordinate.add(radioWGS84);
bgCoordinate.add(radioBeijing54);
bgCoordinate.add(radioXian80);
//添加标签和面板来显示和选择坐标类型
add(new JLabel("选择坐标类型:"));
//将单选按钮添加到 coordinatePanel 中,并将该面板添加到主面板中
JPanel coordinatePanel = new JPanel(new GridLayout(1, 3));
coordinatePanel.add(radioWGS84);
coordinatePanel.add(radioBeijing54);
coordinatePanel.add(radioXian80);
add(coordinatePanel);
//添加标签和文本字段,用于输入经度和纬度
add(new JLabel("输入经度:"));
textLon = new JTextField();
add(textLon);
add(new JLabel("输入纬度:"));
textLat = new JTextField();
add(textLat);
//创建两个单选按钮,用于选择分带类型
radio3Degree = new JRadioButton("3度分带");
radio6Degree = new JRadioButton("6度分带");
//创建一个按钮组 bgDegree,并将这两个单选按钮添加到按钮组中
ButtonGroup bgDegree = new ButtonGroup();
bgDegree.add(radio3Degree);
bgDegree.add(radio6Degree);
//添加标签和面板来显示和选择分带类型
add(new JLabel("选择分带类型:"));
JPanel degreePanel = new JPanel(new GridLayout(1, 2));
//将单选按钮添加到 degreePanel 中,并将该面板添加到主面板中
degreePanel.add(radio3Degree);
degreePanel.add(radio6Degree);
add(degreePanel);
buttonTransform = new JButton("转换");
//创建一个按钮 buttonTransform,用于执行坐标转换
add(buttonTransform);
//添加一个空标签作为占位符,以确保排版合理
add(new JLabel());
//添加标签和文本字段,用于显示转换后的 X 坐标和 Y 坐标
add(new JLabel("X坐标:"));
textX = new JTextField();
//将文本字段设置为不可编辑
textX.setEditable(false);
add(textX);
add(new JLabel("Y坐标:"));
textY = new JTextField();
textY.setEditable(false);
add(textY);
//为转换按钮添加事件监听器,当按钮被点击时,将调用 Controller 类的 actionPerformed 方法
buttonTransform.addActionListener(new Controller());
}
private class Controller implements ActionListener {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
try {
double lon = Double.parseDouble(textLon.getText()); //从文本字段中读取并解析经度和纬度
double lat = Double.parseDouble(textLat.getText());
gs converter;
//根据选择的坐标类型,创建相应的 gs 类实例(转换器)
if (radioWGS84.isSelected()) {
converter = new gs(6378137.0, 6356752.3142);
} else if (radioBeijing54.isSelected()) {
converter = new gs(6378245.0, 6356863.0188);
} else if (radioXian80.isSelected()) {
converter = new gs(6378140.0, 6356755.2882);
} else {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "请选择一种坐标类型");//如果没有选择任何坐标类型,显示错误消息并返回
return;
}
//根据选择的分带类型,使用转换器将经纬度转换为 X 坐标和 Y 坐标
double x, y;
if (radio3Degree.isSelected()) {
x = converter.gsklv3gtransformX(lon, lat);
y = converter.gsklv3gtransformY(lon, lat);
} else if (radio6Degree.isSelected()) {
x = converter.gsklv6gtransformX(lon, lat);
y = converter.gsklv6gtransformY(lon, lat);
} else {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "请选择一种分带类型");//如果没有选择任何分带类型,显示错误消息并返回
return;
}
//将转换结果格式化为字符串并显示在相应的文本字段中,保留11位小数
textX.setText(String.format("%.11f", x));
textY.setText(String.format("%.11f", y));
} catch (NumberFormatException ex) { //捕获 NumberFormatException 异常,如果输入的经纬度值无效,显示错误消息
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "请输入有效的经纬度值");
}
}
}
}GitHub仓库
GitHub仓库:TshiauHuan/GaussKrueger_Transform: XMUT Java课设 高斯克吕格投影正解转换




